What Are Piston Return Springs
What are piston return springs? Piston return springs assist pistons in returning to their starting position, improving mechanical system control and efficiency.
Pistons are a fundamental component in many mechanical systems, playing a crucial role in converting energy into mechanical motion. These versatile devices are found in various industries, from automotive engines to hydraulic systems. However, to ensure their smooth and controlled movement, pistons often rely on a lesser-known but equally important component: piston return springs.
Key Takeaways
Piston return springs are essential components that help ensure smooth and reliable operation in various applications. They are used to force a piston back to its original position after hydraulic pressure is released.
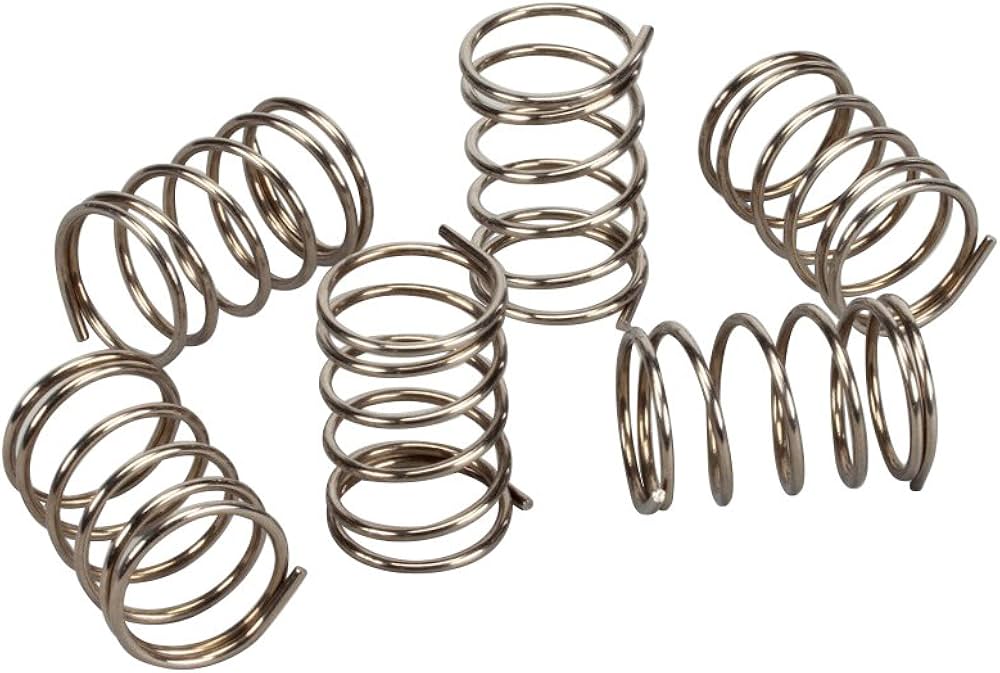
Piston return springs can use disc springs or disc spring stacks. When hydraulic pressure is applied, the disc spring compresses over the piston. Once the hydraulic pressure is released, the spring stack forces the piston back to its original position. The use of disc springs can result in consistently smooth shifting.
Understanding Pistons

Before delving into the specifics of piston return springs, let’s first understand the fundamental role of pistons. Pistons are cylindrical components typically made of metal that move back and forth within a cylinder or chamber. Their primary function is to create a sealed environment within the cylinder, which allows for the conversion of energy.
In the automotive world, for instance, pistons are the heart of an internal combustion engine. When fuel and air are ignited within the engine’s cylinders, pistons move up and down, transferring energy to the crankshaft, which ultimately powers the vehicle. This basic concept applies to various applications, including hydraulic systems, pneumatic devices, industrial machinery, aerospace, and even medical equipment.
The smooth and precise movement of pistons is crucial for the proper functioning of these systems. This is where piston return springs come into play.
The Need for Piston Return Springs
Piston return springs, as the name suggests, are springs specifically designed to assist in the return or retraction of pistons to their original position. While pistons are excellent at generating force during their power stroke (the phase where they move away from their initial position), they require assistance to return swiftly and accurately to their starting point. This is where return springs prove their worth.

Return springs are essential for several reasons. Firstly, they help maintain control over the piston’s movement, preventing it from slamming or overshooting its intended position. In applications where precision is critical, such as automotive engines or hydraulic systems, this control is paramount for system efficiency and safety.
Moreover, return springs contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of the mechanical system. By reducing the impact forces on pistons and other components, they help mitigate wear and tear, ultimately reducing maintenance requirements and downtime.
Types of Piston Return Springs
Piston return springs come in various types, each with its own set of characteristics and applications. Here, we’ll explore the three most common types:

1. Coil Springs
Coil springs are perhaps the most recognizable type of return spring. They consist of a helical coil of wire and are known for their flexibility and durability. Coil springs are widely used in automotive applications, where they provide the necessary force to return engine pistons to their initial position after the power stroke.
One notable advantage of coil springs is their ability to store and release energy efficiently, making them suitable for high-frequency piston movements. Their design allows for easy customization to meet specific force and space requirements.
However, it’s essential to consider factors such as spring rate (stiffness), wire diameter, and coil pitch when selecting coil springs for a particular application.
2. Disc Springs
Disc springs, also known as Belleville washers, are conical or cup-shaped springs that resemble a stack of washers. These springs are excellent at handling heavy loads while maintaining a compact design. They find application in hydraulic systems, where they provide the necessary force to retract pistons in heavy-duty machinery.
Disc springs are known for their progressive spring rate, meaning they offer varying resistance depending on the applied load. This feature can be advantageous in situations where a gradual increase in force is required during the piston’s return.
Additionally, disc springs are highly reliable and have a long service life, making them suitable for demanding industrial environments.
3. Leaf Springs
Leaf springs, also called flat or semi-elliptical springs, consist of several thin, flat plates or “leaves” stacked on top of each other. These springs are widely used in applications where space is limited, such as pneumatic systems and some industrial machinery.
One of the primary advantages of leaf springs is their ability to provide a significant amount of force in a compact form factor. They are also known for their straightforward installation and cost-effectiveness.
However, leaf springs have limitations in terms of flexibility and customization. They may not be the best choice for applications requiring precise control over the piston’s return speed and force.
Design and Function of Piston Return Springs

To understand how piston return springs work, let’s examine their design and function in more detail. The fundamental principle behind these springs is elastic potential energy. When the piston is pushed away from its initial position (the power stroke), it compresses the return spring. This compression stores potential energy within the spring.
As the external force on the piston is released or reduced, the potential energy stored in the spring is converted back into kinetic energy, pushing the piston back towards its original position. This controlled release of energy ensures that the piston returns smoothly and precisely, preventing any abrupt or uncontrolled movements.
The design of a piston return spring must consider several factors, including:
- Spring Rate: This refers to the stiffness of the spring and determines how much force is required to compress it. The spring rate should be chosen to match the specific application’s requirements, ensuring that the piston returns at the desired speed and with the necessary force.
- Materials: Springs are typically made from materials like steel, which offer excellent durability and resilience. The choice of material depends on factors such as temperature, corrosion resistance, and load capacity.
- Size and Shape: The physical dimensions of the spring must fit within the available space in the mechanical system. Additionally, the spring’s shape may influence its performance.
- End Configuration: How the spring is attached to the piston and the surrounding structure can impact its effectiveness. Proper attachment ensures that the spring functions as intended.
Common Applications of Piston Return Springs
Piston return springs are employed in a wide range of applications across various industries:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive world, piston return springs are integral to internal combustion engines. They assist in returning engine pistons to their starting position after the power stroke, ensuring that the engine can continue to operate smoothly and efficiently.
Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic systems, commonly used in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and industrial presses, rely on piston return springs to control the movement of hydraulic pistons. These springs contribute to the precise and controlled operation of these systems.
Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems, found in manufacturing processes and automated machinery, use compressed air to generate motion. Piston return springs play a vital role in regulating the movement of pneumatic pistons, enabling the automation of various tasks.
Industrial Machinery
A wide array of industrial machinery, including pumps, compressors, and material handling equipment, utilizes piston return springs. These springs help ensure the reliability and efficiency of these critical machines.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace applications demand precision and reliability. Piston return springs are used in various aerospace systems, including landing gear mechanisms and flight control systems, to ensure the safe and controlled movement of components.
Medical Devices
Piston return springs are even found in medical equipment such as infusion pumps and diagnostic instruments. In these applications, precision and consistency are paramount to patient safety and device effectiveness.

Benefits of Using Piston Return Springs
The incorporation of piston return springs into mechanical systems offers several significant advantages:
- Improved System Reliability: By providing controlled and predictable piston movement, return springs enhance the overall reliability of the system. This is crucial in applications where downtime or malfunctions can have costly consequences.
- Enhanced Performance and Efficiency: Return springs ensure that pistons return to their initial positions swiftly and accurately. This, in turn, contributes to the overall performance and efficiency of the system, reducing energy waste and improving productivity.
- Reduction in Maintenance and Downtime: The controlled movement facilitated by return springs reduces the wear and tear on pistons and other components. As a result, maintenance requirements are minimized, leading to reduced downtime and lower operational costs.
- Safety Considerations: In applications where safety is a primary concern, such as automotive braking systems or aerospace controls, piston return springs play a critical role in ensuring that components move in a controlled and predictable manner, enhancing overall safety.
Challenges and Considerations
While piston return springs offer numerous benefits, they are not without their challenges and considerations:
- Common Issues: Like any mechanical component, return springs can experience wear and fatigue over time. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to address issues such as spring breakage or loss of elasticity.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Replacing piston return springs may require disassembly of the mechanical system, leading to downtime. Proper planning and scheduling of maintenance activities are essential to minimize disruptions.
- Temperature and Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions can affect the performance of piston return springs. Selecting springs made from appropriate materials and coatings is crucial in such situations.
Conclusion
In the world of mechanical systems, where precision, reliability, and control are paramount, piston return springs quietly play a vital role. These unassuming components ensure that pistons move in a controlled and predictable manner, contributing to the efficiency, safety, and longevity of various industrial applications.
Whether it’s the reliable operation of an automotive engine, the precision of a hydraulic press, or the safety of an aerospace control system, piston return springs silently uphold the integrity of these complex mechanical systems. Understanding their function and selecting the right type of return spring for a specific application is a key step in optimizing performance and ensuring the continued success of these essential technologies.
As we continue to advance technologically and demand greater efficiency and safety from our machines, the role of piston return springs will remain as crucial as ever. It’s an often-overlooked but indispensable component in the intricate dance of mechanical systems, ensuring that everything moves in harmony.
FAQ:
How do return springs work?
Return springs store energy when compressed and release it to help pistons return to their starting position, ensuring controlled movement in various mechanical systems.
What is the purpose of the return spring in front of the master cylinder piston?
The return spring in front of the master cylinder piston ensures that the piston returns smoothly and precisely, enhancing the control and reliability of the braking system.
What is a piston that moves back and forth in an engine?
A piston in an engine is a cylindrical component that moves up and down within a cylinder, converting energy from fuel combustion into mechanical motion.
Do all cars have piston rings?
Yes, nearly all internal combustion engines in cars use piston rings. These rings provide a seal between the piston and cylinder wall, ensuring proper compression and reducing oil consumption.














![What's Included in F-150 Tremor® Package: [Complete Guide] 51 What Is Included In F150 Tremor Package](https://roadmomentum.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/0.jpg)

