How Far Can I Drive With A Bad Alternator
Your vehicle’s alternator is a vital component of its electrical system, playing a crucial role in powering various electrical components and charging the battery. When the alternator starts to fail, it can leave you with some daunting questions, such as, “How far can I drive with a bad alternator?” This article aims to shed light on this question while emphasizing the importance of addressing alternator issues promptly.
Signs of a Failing Alternator
Before delving into how far you can drive with a failing alternator, it’s essential to recognize the signs of trouble. Identifying these symptoms early can save you from potentially dangerous situations on the road.
Dimming Headlights and Electrical Issues:
One of the first signs of a failing alternator is often dimming headlights. You may also notice dimming or flickering interior lights, erratic power window operation, or other electrical problems.
Strange Noises and Warning Lights:
Unusual noises coming from the engine, such as grinding or squealing, can indicate alternator issues. Additionally, dashboard warning lights, such as the battery or alternator warning light, may illuminate.
Difficulty Starting the Vehicle:
A weak or failing alternator can result in difficulty starting the vehicle, especially in cold weather. You may hear a clicking sound when turning the key, which is a sign of insufficient electrical power.
How an Alternator Works
To understand the implications of driving with a bad alternator, it’s essential to grasp how this critical component functions.
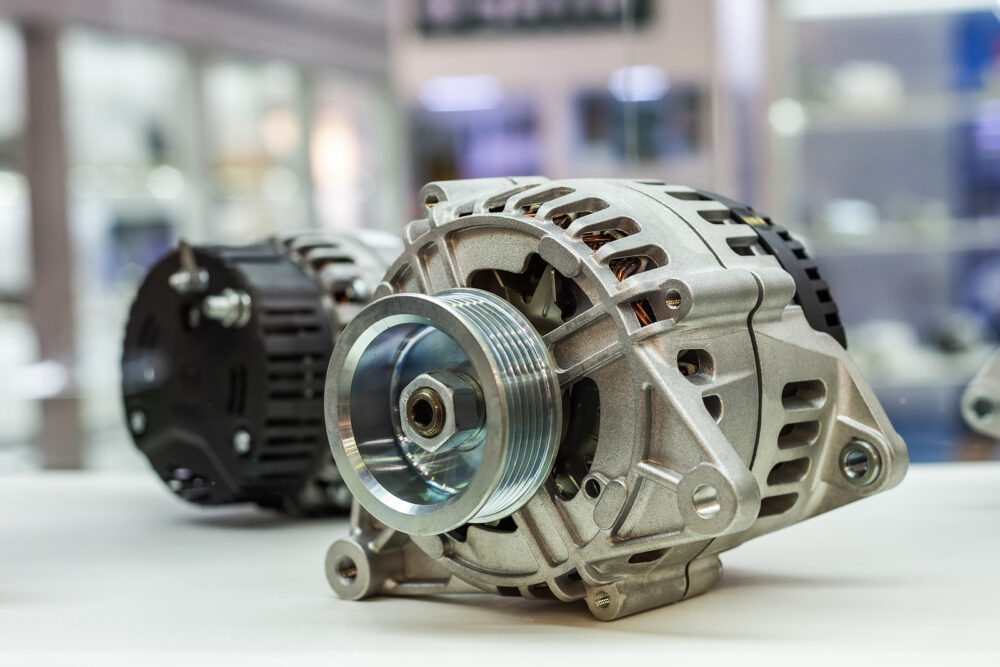
The alternator is essentially a generator powered by the engine’s belt drive system. Its primary purpose is to convert mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This electrical energy is then used to power various electrical components in the vehicle and recharge the battery.
The alternator works in tandem with the battery. While the battery supplies power to start the engine and provides electricity when the engine is off, the alternator takes over when the engine is running, ensuring a constant supply of electrical power.
Factors Affecting How Far You Can Drive

The distance you can drive with a bad alternator largely depends on several factors, including:
- Battery Health and Capacity: A healthy battery can store more electrical energy and potentially allow you to drive farther with a failing alternator. However, if the battery is weak or nearing the end of its life, your driving range will be limited.
- Electrical Load on the Vehicle: Modern vehicles are equipped with various electrical components, from the radio and air conditioning to power windows and heated seats. The more electrical accessories you use while driving, the faster your battery will drain when the alternator is not functioning correctly.
- Existing Charge in the Battery: If your battery is fully charged when the alternator starts to fail, you may have more time before the battery becomes depleted. However, if the alternator fails when the battery is already partially discharged, your driving range will be considerably shorter.
- Driving Conditions and Habits: Factors like traffic congestion, frequent stops and starts, and driving in hilly terrain can all affect how far you can drive with a bad alternator. Stop-and-go driving and idling consumes more electrical power.
Risks of Driving with a Bad Alternator
While it may be tempting to push the limits and continue driving with a failing alternator, doing so comes with significant risks and potential consequences.
- Battery Depletion and Dead Battery: The most immediate risk is that your battery will become depleted. Once the battery is drained, your vehicle will stall, and you’ll be stranded. Jump-starting the car may be a temporary solution, but it won’t fix the underlying alternator problem.
- Stranded on the Road: If your vehicle stalls due to a dead battery, you’ll find yourself stranded on the road. This can be not only inconvenient but also potentially dangerous, depending on your location and the time of day.
- Potential for Damaging Other Vehicle Components: A failing alternator can send irregular voltage to various electrical components. This fluctuation in voltage can damage sensitive electronics, such as the engine control module or the radio.
- Safety Concerns: Driving at night with dimming headlights or without functioning brake lights due to an electrical issue poses significant safety risks to you and other road users. Ensuring your vehicle’s safety features are fully operational is paramount.
Tips for Extending Your Drive with a Bad Alternator
If you find yourself in a situation where you must drive with a failing alternator, consider these tips to maximize your driving range and minimize risks:
- Reduce Electrical Load: Turn off all non-essential electrical accessories, including the radio, air conditioning, and heated seats. Limit the use of power windows and other power-hungry features.
- Charge the Battery Intermittently: If you can safely do so, pull over and let the engine idle for a few minutes. This can provide a brief recharge to the battery and extend your driving range.
- Keep an Emergency Kit in the Vehicle: Always carry essential items in your vehicle, such as jumper cables, a flashlight, and a portable phone charger. These tools can be invaluable if you experience a battery-related issue on the road.
- Plan Short Trips Carefully: If you’re aware of a failing alternator, avoid long trips and plan your routes to minimize driving time. Stick to routes with easy access to help if needed.
When to Seek Professional Help
While these tips can help you extend your drive with a failing alternator, they are not a long-term solution. It’s crucial to recognize that a bad alternator requires professional attention. Here’s when to seek help:
- As soon as Symptoms Appear: If you notice any of the signs of a failing alternator mentioned earlier, it’s advisable to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic promptly. Early diagnosis can prevent further damage.
- When the Battery Light Illuminates: If the battery or alternator warning light on your dashboard comes on, it’s a clear indicator of a charging system problem. Don’t ignore this warning; consult a mechanic immediately.
- When the Battery Is Frequently Dead: Repeatedly needing jump-starts or experiencing dead battery issues is a clear sign that your alternator is not functioning correctly. Have it checked and repaired promptly to avoid future inconveniences?
- When You Experience Electrical Problems: Any unusual electrical issues in your vehicle, such as flickering lights or erratic behavior, should be investigated by a professional.
Conclusion
Driving with a bad alternator is a risky endeavor that should be avoided whenever possible. While you may be able to drive for a short distance with a failing alternator, the risks of battery depletion, vehicle stalling, and potential damage to other components make it an unwise choice. If you suspect alternator issues or notice any warning signs, seek the expertise of a qualified mechanic promptly. Your safety and the reliability of your vehicle depend on it. Remember, responsible vehicle maintenance and timely repairs are key to trouble-free and safe driving experiences.
FAQ:
Can you drive long distances with a bad alternator?
It’s not advisable to drive long distances with a bad alternator due to the risk of battery depletion and potential breakdown.
How long will a battery last if the alternator is bad?
The battery’s lifespan when the alternator is bad varies depending on factors like battery health and electrical load but is generally limited to a few hours to a day.
How long will a car run off the alternator?
A car can run off the alternator while the engine is running, but it cannot sustain the vehicle once the engine is turned off.
Will driving with a bad alternator ruin your battery?
Yes, driving with a bad alternator can lead to a depleted battery, potentially causing damage or shortening the battery’s lifespan.